The Basics of a CPU
A CPU processes instructions from programs. It turns data into actions you see on screen. Think of it as a super-fast calculator that follows steps.
Why learn about CPUs? They power everything from phones to supercomputers. Knowing them helps you pick better devices or fix simple issues.
History of the CPU: From Big Machines to Tiny Chips
CPUs started long ago. In 1945, ENIAC used vacuum tubes for processing. These were huge and hot. Then, in 1947, transistors came along. They made things smaller and cooler.
In 1971, Intel made the 4004 microprocessor. This tiny chip fit a whole CPU on one piece of silicon. It changed everything. Personal computers like the IBM PC in 1981 became common.
Moore’s Law from 1965 said transistors double every two years. This made CPUs faster. By the 2000s, multi-core CPUs arrived. Now, in 2026, CPUs have AI cores and handle billions of tasks per second.
Here’s a quick timeline:
- 1940s: Vacuum tubes in ENIAC.
- 1950s: Transistors replace tubes.
- 1970s: First microprocessors like Intel 4004.
- 1980s: Personal CPUs in home computers.
- 2000s: Multi-core designs for better speed.
- 2020s: AI and quantum hints.
This evolution shrank CPUs from room-size to fingernail-size. Today, over 6.8 billion smartphones use advanced processors.
How Does a CPU Work?
A CPU follows a cycle: fetch, decode, execute, store. It grabs instructions from memory, figures them out, does the work, and saves results.
Key parts inside:
- Control Unit (CU): Directs traffic. It tells other parts what to do.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): Handles math and logic. Adds numbers or compares values.
- Registers: Tiny storage spots for quick data access.
- Cache: Fast memory inside the CPU for often-used info.

The CPU connects to the motherboard via a socket. It works with RAM for temporary data and storage like SSDs for long-term files.
In action: When you click a button, the CPU gets the command, processes it, and shows the result. This happens billions of times a second, measured in gigahertz (GHz). A 3 GHz CPU does 3 billion cycles per second.
Inside the CPU: Cores, Cache, and More
Modern CPUs have multiple cores. Each core acts like a mini-CPU. A quad-core has four, great for multitasking.
- Cores: More mean better performance. Servers use up to 128 cores.
- Threads: Allow one core to handle two tasks at once via multi-threading.
- Cache Size: Levels like L1, L2, L3 store data close. Bigger cache speeds things up.
- Clock Speed: How fast it runs, in GHz. Higher is faster, but needs good cooling.
CPUs also include integrated GPUs for basic graphics. For gaming, pair with a separate GPU.
Types of CPUs
CPUs vary by use:
- Desktop CPUs: Powerful for home PCs. Examples: Intel Core i9 or AMD Ryzen 9.
- Mobile CPUs: Efficient for laptops and phones. Use less power, like ARM designs.
- Server CPUs: Handle heavy loads. Think Intel Xeon or AMD EPYC with many cores.
- Embedded CPUs: In cars or appliances. Small and specialized.
Choose based on needs. Gamers want high cores; office users need basics.
Popular CPU Brands and Comparisons
Intel and AMD lead the market. ARM powers most mobiles.
- Intel: Known for Core series. Strong in single-thread tasks.
- AMD: Ryzen line offers value with more cores.
- ARM: Efficient for phones, like in Apple Silicon.
In 2026, AMD Ryzen 9000 series hits high speeds with AI features. Intel Core Ultra 200V focuses on efficiency.
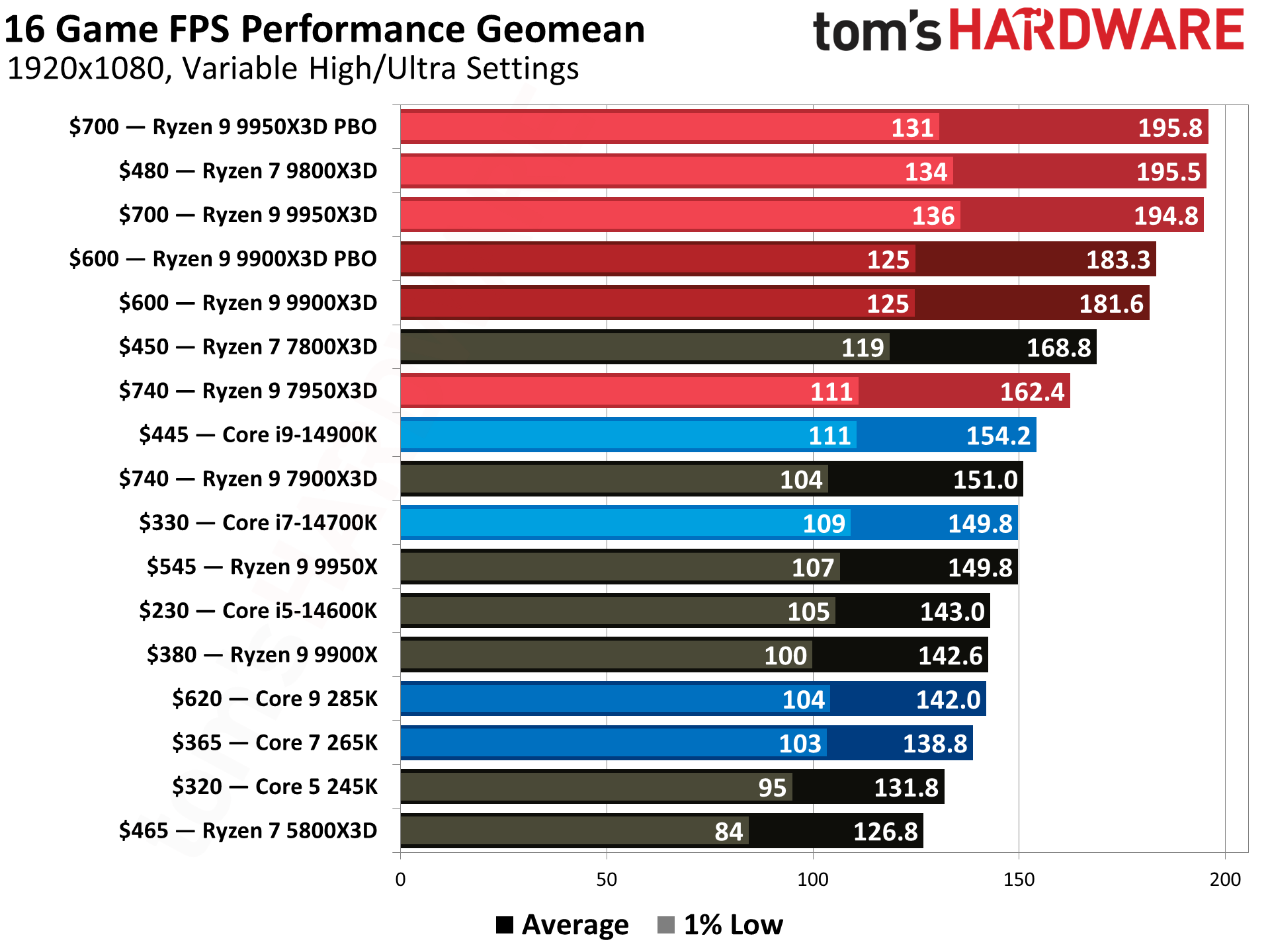
Stats show AMD gaining 30% market share in desktops. Pick Intel for stability, AMD for multitasking.
CPU Performance Factors
Speed isn’t just GHz. Consider:
- Cores and Threads: For video editing, more is better.
- Cache: Reduces wait times.
- Architecture: New designs like 3D-stacked improve efficiency.
- Power Use: Measured in TDP (watts). Lower for laptops.
Overclocking boosts speed but needs cooling. Always check compatibility with your motherboard.
How CPU Fits in a Computer
The CPU works with other parts. It sits on the motherboard, connected to RAM and storage. For full setup, see guides on what makes a computer.
It processes data from input like keyboards, sends to output like screens. Buses carry info between parts.
In gaming, CPU handles AI while GPU does visuals. Balanced systems run smooth.
Future of CPUs
By 2030, expect quantum bits and more AI integration. Trends:
- Smaller transistors (2nm nodes).
- Edge computing for faster local processing.
- Sustainable designs with less power.
Challenges include heat and shortages, but innovations like liquid cooling help.
Common CPU Issues and Tips
Overheating? Clean fans. Slow performance? Update drivers.
Tips:
- Use thermal paste for better heat transfer.
- Monitor temps with software.
- Upgrade every 5 years for best speed.
If building a PC, start with a good CPU. Visit Biz Reporterz for more tech news.
FAQs About What Is a CPU? Complete Beginner’s Guide to Computer Processors?
What does CPU stand for? Central Processing Unit.
How many cores do I need? For basics, 4-6. For pro work, 8+.
What’s the difference between CPU and GPU? CPU handles general tasks; GPU focuses on graphics.
Can I upgrade my CPU? Yes, if socket matches.
Why is my CPU hot? Poor cooling or heavy use. Add fans.
Conclusion
In this What Is a CPU? Complete Beginner’s Guide to Computer Processors?, we covered basics, history, workings, and future. The CPU powers your digital world, evolving from bulky machines to smart chips. With right knowledge, you choose wisely.
What do you use your CPU for most? Share below!
References
- What Parts Make a Modern Computer – Details on computer components and trends for beginners and tech enthusiasts.
- CPU Glossary by ARM – Technical definitions and selection tips for developers and students.
- What Is a Computer? – Overview of computers, history, and parts for new learners aged 10+.